This tutorial will explain how to use our NerdGraph API to set up your topology. Topology configuration allows your alert decisions to better correlate incidents.
Requirements
Topology correlation is currently in limited release. See topology requirements.
To use NerdGraph, you'll need a user key.
Overview of tutorial
With New Relic’s alerts, you can create custom decisions that govern how your incidents are correlated. One kind of custom decision logic uses the concept of "topology," which is a representation of your service map: how the services and resources in your infrastructure relate to one another.
This tutorial will show you how to use NerdGraph to:
- Set up your topology by creating vertices and edges
- Delete vertices and edges
- Retrieve topology data
Before using NerdGraph to configure your topology, you should have a basic understanding of:
- What correlated decisions are and how topology correlation works.
- The topology structure you're trying to implement. One way to understand this is to use our service map feature to see how entities in your infrastructure relate to each other.
- What NerdGraph is and how to use the NerdGraph API explorer to run queries.
Mutation examples
In NerdGraph, mutations are requests that perform an action (learn more about NerdGraph terminology), such as creating a resource or changing a configuration.
In this section, we’ll show you how to use aiTopologyCollector mutations to create, edit, or delete your topology.
In the create sections, we’ll create vertices and edges to represent this service map:
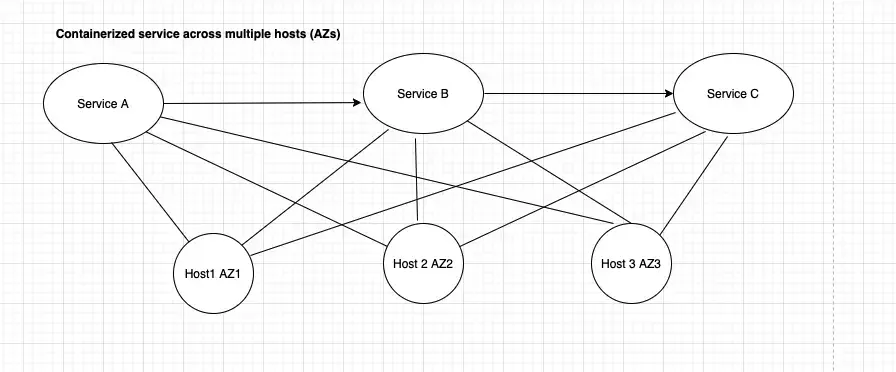
This tutorial uses NerdGraph to create vertices and edges that represent these entities and their relationships.
Create vertices
The following mutation creates one or more vertices, which represent your monitored entities, and are the source from which your incidents come from.
The NerdGraph call below uses the following fields:
accountId: Your New Relic account ID.name: The name of the vertex. This value is case sensitive and must be unique within the graph.vertexClass: The vertex class can beapplication,host,cloud service,cluster, ordatastore. This classification allows your decision logic to restrict your topology-based correlation to restrict vertices matching these classifications.definingAttributes: A set of attributes (key/value pairs) that match an incident event's attributes. These are usually unique identifiers that appear on all incidents, such as entity GUIDs or other IDs. If an incident contains any of the key/value pairs of a vertex’sdefiningAttributes, it’s matched to that vertex. To learn more about attributes and how they can be added, see Add attributes.
Example call:
mutation { aiTopologyCollectorCreateVertices( accountId: NEW_RELIC_ACCOUNT_ID vertices: [ { name: "ServiceA" vertexClass: APPLICATION definingAttributes: [{ key: "application/name", value: "ServiceA" }] } { name: "ServiceB" vertexClass: APPLICATION definingAttributes: [{ key: "application/name", value: "ServiceB" }] } { name: "ServiceC" vertexClass: APPLICATION definingAttributes: [{ key: "application/name", value: "ServiceC" }] } { name: "HOST1" vertexClass: HOST definingAttributes: [ { key: "host/name", value: "HOST1" } { key: "availability-zone", value: "us-west-2a" } { key: "region", value: "us-west-2" } ] } { name: "HOST2" vertexClass: HOST definingAttributes: [ { key: "host/name", value: "HOST2" } { key: "availability-zone", value: "us-west-2b" } { key: "region", value: "us-west-2" } ] } { name: "HOST3" vertexClass: HOST definingAttributes: [ { key: "host/name", value: "HOST3" } { key: "availability-zone", value: "us-west-2c" } { key: "region", value: "us-west-2" } ] } ] ) { result }}Create edges
This mutation is used to create one or more edges, which represent relationships between vertices.
The NerdGraph call below makes use of these fields:
accountId: Your New Relic account ID.fromVertexName: The name of the vertex the edge is starting from.toVertexName: The name of the connecting vertex.directed: A boolean that describes how vertices connect.trueindicates a one-way relationship (for example, one service calling another) andfalseindicates . By default, directed =true.
Example call:
mutation { aiTopologyCollectorCreateEdges( accountId: NEW_RELIC_ACCOUNT_ID edges: [ { directed: true, fromVertexName: "ServiceA", toVertexName: "ServiceB" } { directed: true, fromVertexName: "ServiceB", toVertexName: "ServiceC" } { directed: false, fromVertexName: "ServiceA", toVertexName: "HOST1" } { directed: false, fromVertexName: "ServiceA", toVertexName: "HOST2" } { directed: false, fromVertexName: "ServiceA", toVertexName: "HOST3" } { directed: false, fromVertexName: "ServiceB", toVertexName: "HOST1" } { directed: false, fromVertexName: "ServiceB", toVertexName: "HOST2" } { directed: false, fromVertexName: "ServiceB", toVertexName: "HOST3" } { directed: false, fromVertexName: "ServiceC", toVertexName: "HOST1" } { directed: false, fromVertexName: "ServiceC", toVertexName: "HOST2" } { directed: false, fromVertexName: "ServiceC", toVertexName: "HOST3" } ] ) { result }}Delete vertices
This mutation deletes vertices in your topology graph. Note that deleting a vertex deletes all edges connected to it.
The NerdGraph call below uses these fields:
accountId: Your New Relic account ID.vertexNames: A list of vertex names you want to delete.
Example call:
mutation { aiTopologyCollectorDeleteVertices( accountId: NEW_RELIC_ACCOUNT_ID vertexNames: ["ServiceA", "ServiceB", "ServiceC", "HOST1", "HOST2", "HOST3"] ) { result }}Delete edges
This mutation deletes edges connecting vertices in your topology graph.
The NerdGraph call below uses these fields:
accountId: Your New Relic account ID.edgeIds: A list of edge IDs you want to delete.
Example call:
mutation { aiTopologyCollectorDeleteEdges( accountId: NEW_RELIC_ACCOUNT_ID edgeIds: [ "d8a7971b-575d-42e9-aa13-43a50c5a7d10" "0da5cb92-0428-4890-992b-2823d037cb5e" ] ) { result }}Query examples
In NerdGraph, queries are used to fetch data, as opposed to mutations, which perform actions (learn more about terminology). Nerdgraph queries are not static, meaning that you can ask for more or less data depending on your needs. To retrieve your topology data, you’ll use the aiTopology query.
Retrieve vertices
This query returns a list of vertices in your topology graph.
{ actor { account(id: NEW_RELIC_ACCOUNT_ID) { aiTopology { vertices { vertices { id name definingAttributes { key value } updatedAt vertexClass } count cursor } } } }}Retrieve edges
This query returns a list of edges in your topology graph:
{ actor { account(id: NEW_RELIC_ACCOUNT_ID) { aiTopology { edges { edges { id toVertexName fromVertexName directed updatedAt } cursor count } } } }}